Wellhealthorganic.com: Vegetarian Protein Sources Complete Guide
WellHealthOrganic.com: Vegetarian Protein Sources offers a comprehensive guide to incorporating plant-based protein into your diet. In today’s health-conscious world, the demand for nutritious alternatives to meat-based proteins is on the rise, driven by concerns for health, ethics, and the environment. At WellHealthOrganic.com, we recognize the importance of meeting your protein needs while adhering to a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. From protein-packed legumes and nuts to versatile grains and soy products, our guide explores a diverse array of vegetarian protein sources. Whether you’re a seasoned vegetarian, a committed vegan, or simply looking to incorporate more plant-based foods into your diet, WellHealthOrganic.com provides the insights and resources you need to make informed dietary choices for a healthier, more sustainable lifestyle.
Table of Contents
Introduction To WellHealthOrganic.com: Vegetarian Protein Sources
In today’s health-conscious world, the significance of protein in our diets cannot be overstated. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining overall growth and development. While meat has traditionally been the primary source of protein, a growing number of people are embracing vegetarianism and veganism due to ethical, health, and environmental concerns. This shift has sparked increased interest in vegetarian protein sources, which offer essential nutrients without the need for animal products.
WellHealthOrganic.com is at the forefront of this movement, providing detailed information on high-quality vegetarian protein sources suitable for various dietary preferences. From legumes and nuts to grains and soy products, these plant-based proteins are not only nutritious but also versatile and delicious. Including a variety of protein sources in your diet can help you meet your daily protein needs while enjoying diverse flavors and textures.
This article delves into the top vegetarian protein options, emphasizing their nutritional advantages and practical applications. Whether you are a dedicated vegetarian, a vegan, or simply looking to reduce your meat consumption, WellHealthOrganic.com offers the knowledge and tips you need to make informed dietary choices that promote a healthy, balanced lifestyle.
Why Protein is Essential
Protein is a macronutrient that plays several critical roles in the body. It is composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks for many bodily functions. Here are some key reasons why protein is essential:
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Protein is crucial for repairing damaged muscle tissue and supporting muscle growth, especially after exercise.
- Enzyme and Hormone Production: Proteins help produce enzymes and hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism and mood.
- Immune Function: Proteins are vital for maintaining a healthy immune system, helping the body to fight off infections and illnesses.
- Energy Source: While not the primary source of energy, protein can be used as a fuel source when carbohydrate and fat intake is low.
- Satiety and Weight Management: Protein helps in keeping you full longer, aiding in weight management and reducing overeating.
Common Myths About Vegetarian Protein
Before diving into the best vegetarian protein sources, it’s important to address some common myths:
- Myth 1: Vegetarian diets lack sufficient protein. With careful planning, vegetarian diets can meet and even exceed daily protein requirements.
- Myth 2: Plant proteins are not complete. While some plant proteins may lack one or more essential amino acids, combining different sources can provide all necessary amino acids.
- Myth 3: Vegetarian protein is inferior to animal protein. Plant-based proteins can be just as effective as animal proteins in supporting overall health and fitness.
Top Vegetarian Protein Sources
Legumes
Legumes are a powerhouse of protein and include beans, lentils, and peas. They are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an excellent choice for a balanced diet.
- Beans: Varieties like black beans, kidney beans, and chickpeas are excellent protein sources. For example, a cup of cooked black beans contains about 15 grams of protein.
- Lentils: Lentils come in various colors, such as green, red, and brown, each with a unique flavor and texture. One cup of cooked lentils provides around 18 grams of protein.
- Peas: Green peas and split peas are not only high in protein but also rich in vitamins A, C, and K. A cup of cooked peas offers about 8 grams of protein.
Nuts and Seeds – Compact Nutrient Sources
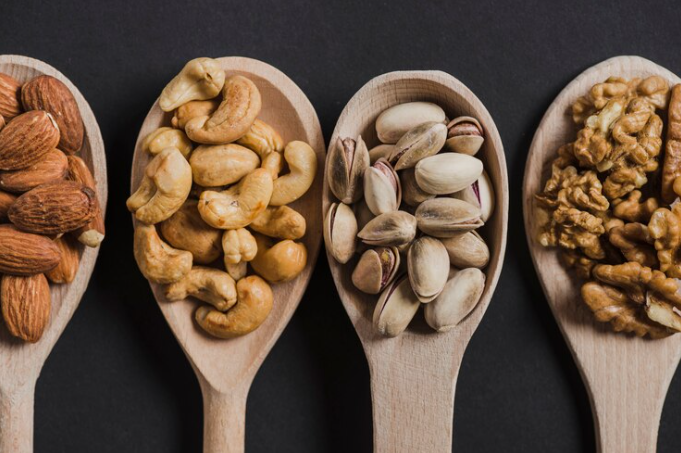

Nuts and seeds are among nature’s most nutrient-dense foods, offering a remarkable array of health benefits in a small package. They are excellent sources of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Incorporating nuts and seeds into your diet can enhance your overall health, provide essential nutrients, and add variety to your meals.
Protein Powerhouses
Nuts and seeds are particularly valued for their protein content. They offer a plant-based alternative to animal proteins, making them an essential component of vegetarian and vegan diets. Here are some standout options:
- Almonds: Almonds are not only high in protein but also rich in vitamin E, magnesium, and healthy fats. An ounce (about 23 almonds) contains around 6 grams of protein.
- Chia Seeds: Despite their small size, chia seeds pack a powerful protein punch with about 4 grams of protein per ounce (around 2 tablespoons). They are also high in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and various micronutrients.
- Pumpkin Seeds: Also known as pepitas, pumpkin seeds are a great protein source with around 7 grams per ounce. They are also rich in iron, magnesium, and zinc.
- Sunflower Seeds: These seeds provide about 6 grams of protein per ounce and are high in vitamin E, selenium, and other antioxidants.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds offer about 5 grams of protein per ounce and are known for their high content of omega-3 fatty acids and fiber.
Healthy Fats and Heart Health
Nuts and seeds are renowned for their healthy fat content, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. These fats help reduce bad cholesterol levels (LDL) and increase good cholesterol levels (HDL), thereby lowering the risk of heart disease.
- Walnuts: Rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid, walnuts support heart health and reduce inflammation. They also provide about 4 grams of protein per ounce.
- Hazelnuts: High in monounsaturated fats, hazelnuts contribute to heart health and provide about 4 grams of protein per ounce.
Vitamins and Minerals
Nuts and seeds are also packed with essential vitamins and minerals that support various bodily functions:
- Magnesium: Crucial for muscle and nerve function, magnesium is abundant in almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds.
- Vitamin E: This powerful antioxidant is found in high amounts in almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts. It helps protect cells from oxidative damage.
- Zinc: Important for immune function and wound healing, zinc is plentiful in pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds.
- Iron: Necessary for oxygen transport in the blood, iron is found in pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, and hemp seeds.
Antioxidants and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Nuts and seeds contain a variety of antioxidants, including polyphenols, which help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation. These properties contribute to lower risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
- Pecans: High in polyphenols, pecans provide antioxidant benefits and contain about 3 grams of protein per ounce.
- Brazil Nuts: A rich source of selenium, an antioxidant mineral that helps protect against oxidative damage and supports thyroid function. Brazil nuts also offer around 4 grams of protein per ounce.
Weight Management and Satiety
The protein and fiber content in nuts and seeds contribute to feelings of fullness and satiety, which can help manage weight by reducing overall calorie intake. Including nuts and seeds in your diet can help curb hunger and prevent overeating.
Versatility in the Diet
Nuts and seeds can be easily incorporated into a variety of dishes, enhancing both their nutritional value and flavor. Here are some ideas:
- Snacks: Enjoy a handful of mixed nuts or seeds as a convenient, protein-rich snack.
- Salads: Sprinkle chia seeds, sunflower seeds, or chopped nuts over salads for added crunch and nutrition.
- Breakfast: Add nuts and seeds to oatmeal, yogurt, or smoothies for a protein boost.
- Baking: Use ground flaxseeds or chia seeds as egg substitutes in baking recipes. Incorporate nuts into muffins, bread, and cookies for added texture and nutrients.
- Nut Butters: Spread almond butter, peanut butter, or sunflower seed butter on toast or use as a dip for fruits and vegetables.
Grains
Whole grains are an important part of a vegetarian diet, offering protein along with fiber and other vital nutrients.
- Quinoa: Quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. One cup of cooked quinoa provides about 8 grams of protein.
- Brown Rice: While not a complete protein, brown rice is still a good source, offering about 5 grams of protein per cup when cooked.
- Oats: Oats are a great breakfast option, providing about 6 grams of protein per cup when cooked.
Soy Products
Soy is a versatile and protein-rich food source that is a staple in many vegetarian and vegan diets.
- Tofu: Made from soybeans, tofu is highly versatile and can be used in a variety of dishes. It provides about 10 grams of protein per half-cup serving.
- Tempeh: Tempeh is made from fermented soybeans and has a firm texture. It offers about 21 grams of protein per cup.
- Edamame: These are young soybeans that are usually steamed or boiled. One cup of cooked edamame provides around 17 grams of protein.
Dairy Alternatives
For those who include dairy in their vegetarian diet or seek plant-based alternatives, there are several high-protein options.
- Greek Yogurt: A rich source of protein, with about 10 grams per 100 grams serving.
- Cottage Cheese: Contains about 11 grams of protein per 100 grams serving.
- Plant-Based Milks: Options like soy milk can offer around 8 grams of protein per cup.
Vegetables
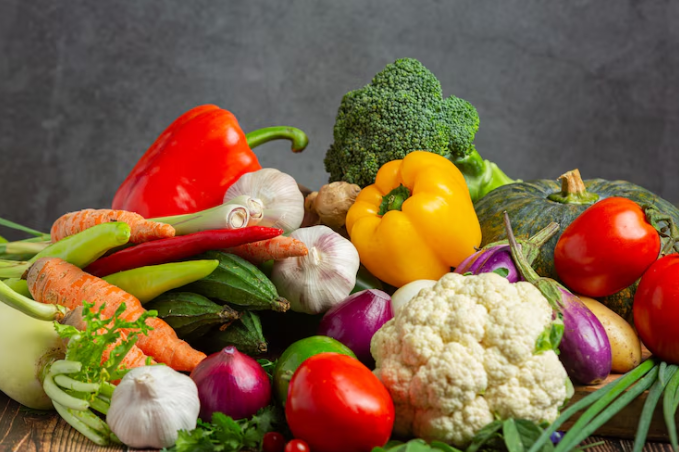

Certain vegetables also provide a good amount of protein and are essential for a well-rounded diet.
- Broccoli: Offers about 4 grams of protein per cup when cooked.
- Spinach: Provides around 5 grams of protein per cooked cup.
- Brussels Sprouts: Contain about 4 grams of protein per cooked cup.
Combining Protein Sources
To ensure you’re getting all essential amino acids, it’s beneficial to combine different protein sources. Here are some effective combinations:
- Rice and Beans: Together, they form a complete protein, providing all essential amino acids.
- Hummus and Whole Wheat Bread: Combining legumes with grains enhances the protein quality.
- Tofu and Quinoa: Both are excellent sources of protein and can be combined in various dishes for a nutrient-packed meal.
Benefits of Vegetarian Protein Sources
Switching to vegetarian protein sources offers numerous benefits:
- Health Benefits: Plant-based proteins are often lower in saturated fat and cholesterol compared to animal proteins, reducing the risk of heart disease and certain cancers.
- Digestive Health: High fiber content in many vegetarian protein sources aids in digestion and prevents constipation.
- Weight Management: Plant-based proteins can help with weight management due to their satiating effect and lower calorie density.
- Sustainability: Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Vegetarian Protein into Your Diet
- Meal Planning: Plan your meals to include a variety of protein sources throughout the week.
- Snack Smart: Opt for protein-rich snacks like nuts, seeds, and hummus with veggies.
- Experiment with Recipes: Try new recipes that incorporate different vegetarian protein sources to keep your diet interesting and flavorful.
- Use Protein Supplements: If necessary, consider plant-based protein powders to supplement your protein intake.
Recipes Featuring Vegetarian Protein Sources
Quinoa and Black Bean Salad
Ingredients:
- 1 cup quinoa
- 2 cups water
- 1 can black beans, rinsed and drained
- 1 red bell pepper, diced
- 1 small red onion, diced
- 1 cup corn kernels
- 1/4 cup fresh cilantro, chopped
- Juice of 2 limes
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- Rinse the quinoa under cold water.
- In a medium pot, bring water to a boil. Add quinoa, reduce to a simmer, cover, and cook for 15 minutes.
- In a large bowl, combine cooked quinoa, black beans, bell pepper, red onion, corn, and cilantro.
- In a small bowl, whisk together lime juice, olive oil, salt, and pepper.
- Pour the dressing over the quinoa mixture and toss to combine.
- Serve chilled or at room temperature.
Tofu Stir-Fry with Vegetables
Ingredients:
- 1 block firm tofu, drained and cubed
- 2 tablespoons soy sauce
- 1 tablespoon sesame oil
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 inch ginger, minced
- 1 red bell pepper, sliced
- 1 broccoli head, cut into florets
- 1 carrot, julienned
- 2 green onions, sliced
- Cooked brown rice
Instructions:
- In a bowl, marinate tofu cubes in soy sauce for at least 15 minutes.
- In a large pan, heat sesame oil over medium heat. Add garlic and ginger, sauté for 1 minute.
- Add marinated tofu and cook until golden brown, about 5 minutes.
- Add bell pepper, broccoli, and carrot. Stir-fry for another 5-7 minutes until vegetables are tender.
- Garnish with green onions and serve over cooked brown rice.
Quinoa – The Complete Protein Grain
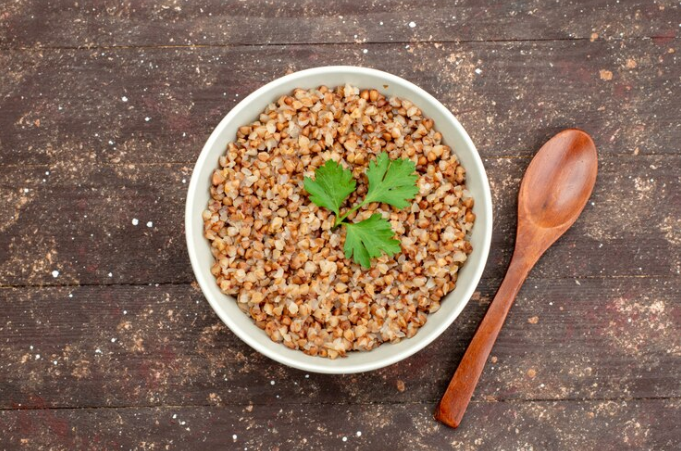

Quinoa, often referred to as a “superfood” or “supergrain,” has gained immense popularity in recent years, especially among health-conscious individuals and those following vegetarian or vegan diets. Known for its impressive nutritional profile, quinoa is unique among plant-based foods as it is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids required by the human body. This makes quinoa an excellent protein source for those looking to reduce or eliminate animal products from their diets.
Nutritional Profile of Quinoa
Quinoa is not only high in protein but also rich in various other nutrients that contribute to its superfood status:
- Protein: One cup of cooked quinoa provides about 8 grams of protein.
- Fiber: Quinoa is an excellent source of dietary fiber, offering about 5 grams per cup. This promotes digestive health and helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Quinoa is rich in vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, folate, and B vitamins. These nutrients are essential for energy production, bone health, and cellular function.
- Antioxidants: Quinoa contains a variety of antioxidants, including flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Low Glycemic Index: With a low glycemic index, quinoa helps regulate blood sugar levels and is beneficial for those managing diabetes or insulin resistance.
Health Benefits of Quinoa
1. Complete Protein Source
One of quinoa’s most notable benefits is its status as a complete protein. Unlike most plant-based foods, quinoa contains all nine essential amino acids, making it comparable to animal-based proteins. This is particularly advantageous for vegetarians and vegans, as it ensures they receive all necessary amino acids for muscle repair, growth, and overall health.
2. Supports Digestive Health
The high fiber content in quinoa aids in digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Fiber also supports a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for overall digestive health and immune function.
3. Gluten-Free Alternative
Quinoa is naturally gluten-free, making it an excellent alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. It provides a nutritious substitute for gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye, allowing those on gluten-free diets to enjoy a versatile and nutrient-rich grain.
4. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
The antioxidants found in quinoa, such as quercetin and kaempferol, help reduce inflammation and protect cells from oxidative damage. This can lower the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, and promote overall health and longevity.
5. Supports Weight Management
Quinoa’s high protein and fiber content contribute to feelings of fullness and satiety, which can help manage weight by reducing overall calorie intake. Including quinoa in meals can help curb hunger and prevent overeating, supporting healthy weight loss and maintenance.
Versatility in Cooking
Quinoa’s mild flavor and versatile texture make it easy to incorporate into a wide range of dishes. Here are some popular ways to use quinoa:
1. Salads
Quinoa makes a great base for salads, adding a hearty texture and boosting protein content. Combine cooked quinoa with fresh vegetables, herbs, and a light dressing for a nutritious and satisfying meal.
2. Breakfast
Quinoa can be used as a nutritious breakfast option. Cooked quinoa can be mixed with fruits, nuts, seeds, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup for a delicious and protein-packed breakfast bowl. It can also be used in place of oats for a warm quinoa porridge.
3. Side Dishes
Quinoa can be served as a side dish, much like rice or couscous. It pairs well with a variety of vegetables, legumes, and proteins, making it a versatile addition to any meal. Try seasoning it with herbs, spices, and a squeeze of lemon juice for extra flavor.
4. Main Courses
Quinoa can be used as the main ingredient in dishes such as quinoa-stuffed peppers, quinoa burgers, and quinoa casseroles. Its ability to absorb flavors and maintain a satisfying texture makes it an excellent substitute for meat in vegetarian and vegan recipes.
5. Baking
Quinoa flour, made from ground quinoa seeds, can be used in baking to add nutritional value to bread, muffins, and pancakes. It provides a gluten-free alternative to wheat flour while enhancing the protein content of baked goods.
How to Cook Quinoa
Cooking quinoa is simple and similar to preparing rice:
- Rinse: Rinse the quinoa under cold water to remove its natural coating, called saponin, which can impart a bitter taste.
- Combine: Combine one part quinoa with two parts water or broth in a pot.
- Boil: Bring the mixture to a boil.
- Simmer: Reduce the heat to low, cover, and simmer for about 15-20 minutes until the quinoa is tender and the liquid is absorbed.
- Fluff: Remove from heat and let it sit, covered, for 5 minutes. Fluff with a fork before serving.
Conclusion Of WellHealthOrganic.com: Vegetarian Protein Sources:
Embracing vegetarian protein sources is not only beneficial for your health but also for the environment. By incorporating a variety of plant-based proteins into your diet, you can meet your nutritional needs while enjoying diverse and delicious meals. WellHealthOrganic.com is dedicated to providing you with the information and resources you need to make informed dietary choices. Whether you’re a lifelong vegetarian, a vegan, or simply looking to reduce your meat consumption, this comprehensive guide will help you on your journey to a healthier, more sustainable lifestyle.
FAQs About WellHealthOrganic.com: Vegetarian Protein Sources
What is quinoa, and why is it considered a superfood?
Quinoa is a nutrient-dense grain known for its high protein content and a range of vitamins and minerals. It is considered a superfood because it provides all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source, along with other beneficial nutrients like fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
How much protein is in quinoa?
One cup of cooked quinoa contains about 8 grams of protein. Unlike most plant-based foods, quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
What are the health benefits of eating quinoa?
Quinoa offers numerous health benefits, including supporting muscle repair and growth, aiding digestion with its high fiber content, providing essential vitamins and minerals, reducing inflammation with antioxidants, and promoting weight management due to its protein and fiber content.
Is quinoa gluten-free?
Yes, quinoa is naturally gluten-free, making it an excellent grain alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. It can be used in various gluten-free recipes to add nutritional value.
How do you cook quinoa?
To cook quinoa, rinse it under cold water to remove its bitter coating. Combine one part quinoa with two parts water or broth in a pot, bring to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer for 15-20 minutes until the quinoa is tender and the liquid is absorbed. Let it sit covered for 5 minutes before fluffing with a fork.
Can quinoa help with weight management?
Yes, quinoa can aid in weight management due to its high protein and fiber content, which promote feelings of fullness and satiety. This helps reduce overall calorie intake and can prevent overeating.
What are some ways to incorporate quinoa into my diet?
Quinoa can be used in various dishes, including salads, breakfast bowls, side dishes, main courses, and baked goods. It pairs well with vegetables, legumes, fruits, nuts, and seeds, making it a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory recipes.
Why is quinoa considered a complete protein?
Quinoa is considered a complete protein because it contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body needs for protein synthesis but cannot produce on its own. This makes it a unique and valuable protein source, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
Are there different types of quinoa?
Yes, there are several types of quinoa, including white, red, and black quinoa. Each type has a slightly different flavor and texture, but they all provide similar nutritional benefits.
What nutrients are found in quinoa besides protein?
Quinoa is rich in various nutrients, including dietary fiber, vitamins (such as B vitamins and vitamin E), and minerals (such as magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and iron). It also contains antioxidants like quercetin and kaempferol, which help reduce inflammation and protect cells from damage.
How does quinoa support digestive health?
Quinoa supports digestive health due to its high fiber content, which promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. The fiber also helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for overall digestive and immune health.
Can quinoa be used in baking?
Yes, quinoa can be used in baking. Quinoa flour, made from ground quinoa seeds, can be used as a gluten-free alternative to wheat flour. It enhances the protein content and nutritional value of baked goods like bread, muffins, and pancakes.
If you found our content (WellHealthOrganic.com: Vegetarian Protein Sources) helpful don’t forget to share it on your social media: Twitter